4.
Kolbe’s
Electrolysis
This is an electrolytic
decarboxylation of carboxylic acids. The mechanism involves the formation and
coupling of alkyl radicals to form a C-C bond.
5.
Organometallic
Reactions
Organometallic compounds possess a
nucleophilic carbon atom which reacts with variety of compounds having
electrophilic carbons to form C-C bonds. Some of the most common organometallic
compounds used are Grignard reagent, organo lithium, organosodium, organozinc,
and organocopper reagents.
a.
Reaction
with Carbonyl Compounds
b.
Reaction
with a,b-unsaturated
carbonyl compounds
Different organometallic compounds react differently
with unsaturated carbonyl compounds. The nucleophilic carbon may attack the
carbonyl carbon (direct addition) or the b-carbon
(conjugate addition or Michael addition).
c.
Reaction
with Epoxide
Organometallic compounds
opens the epoxide ring.
6.
Claisen
Condensation
The self-condensation of esters is known as Claisen
condensation. A common example is the acetoacetic ester synthesis.
7.
Cross
Coupling Reactions
Some important coupling reactions are Suzuki coupling,
Stille coupling, Hiyama coupling, Nigishi coupling, Heck reaction, and Kumada
couplings. All of these reactions involve the formation of a single bond
between carbon atoms.
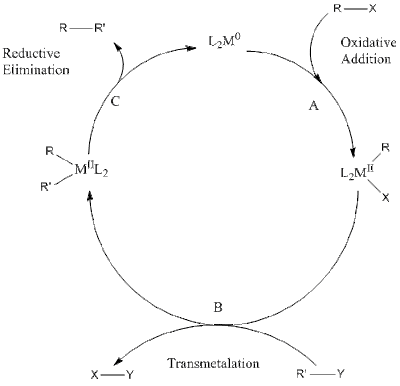
The mechanism of these cross coupling reactions
involve some common steps, viz. oxidative addition, transmetallation, and
reductive elimination.





No comments:
Post a Comment